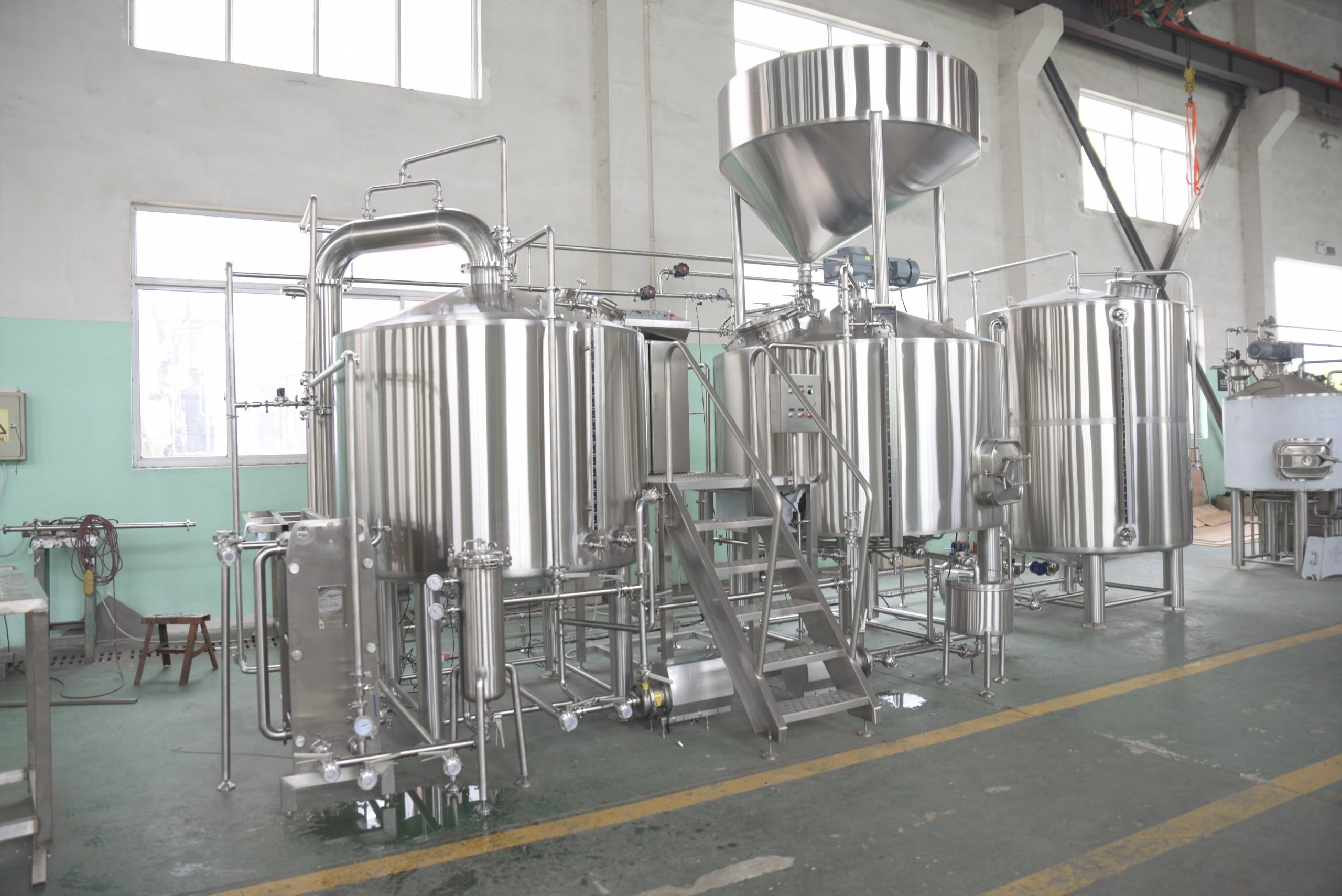
Combination Mash/Lauter Tun VS. Separate Tanks
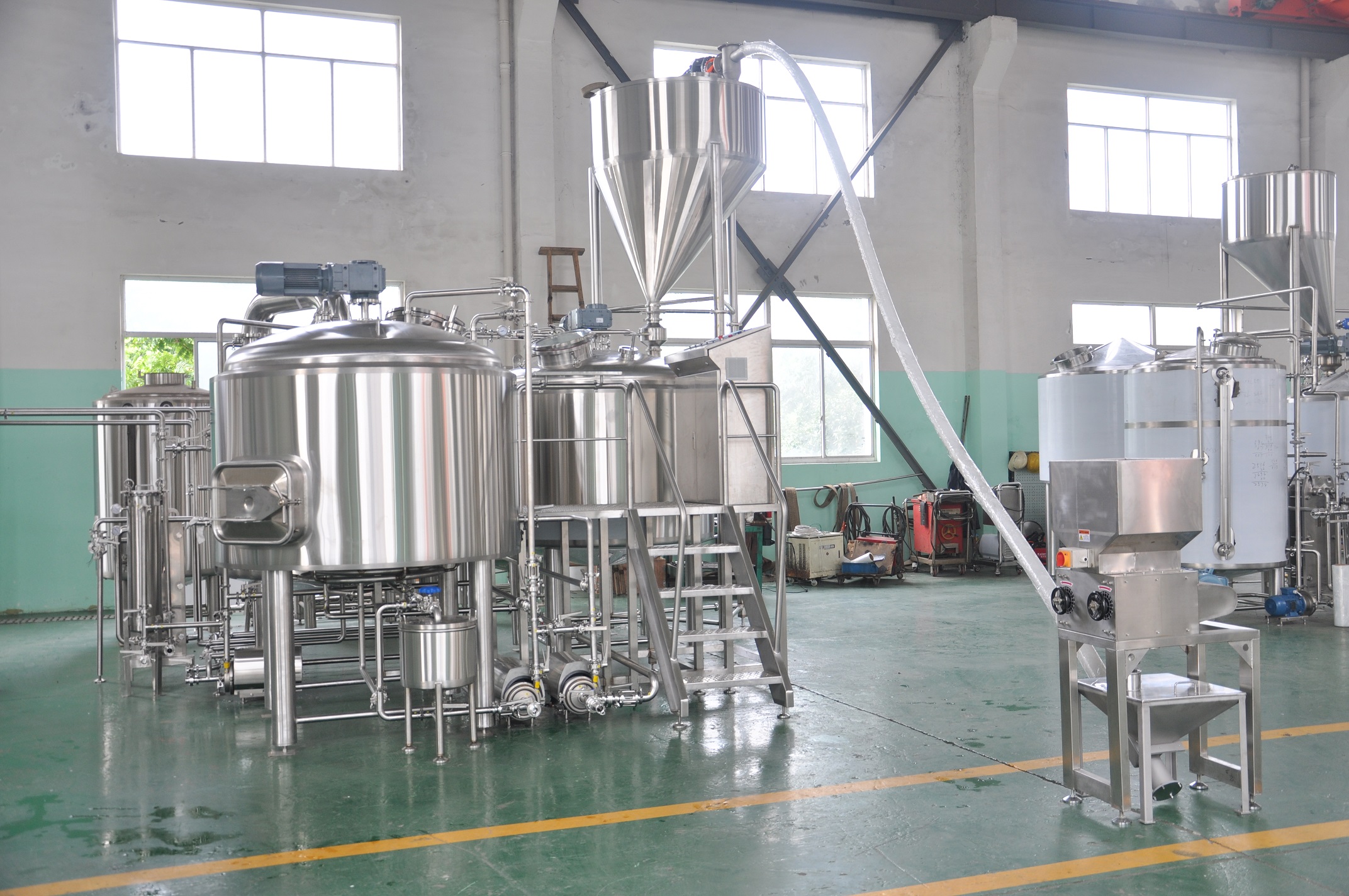

The choice between combination mash/lauter tanks and separate tanks in a brewery depends on various factors, including the brewing process, equipment availability, space constraints, and the desired level of control over the brewing process.
What is a mash/lauter tun?
A mash/lauter tun is a vessel used in the brewing process to carry out the mashing and lautering steps, which are crucial in extracting fermentable sugars from malted grains. It is a key component of a brewery’s brewhouse.
The mash/lauter tun typically features a domed or conical-shaped vessel with an outlet or drain at the bottom to collect the wort. It may also have a raking mechanism or a rotating arm with paddles to agitate the mash during mashing and facilitate the lautering process. Additionally, the mash tun may have temperature controls, valves, and sparging equipment to regulate the mashing and lautering operations.
The mash/lauter tun plays a critical role in extracting fermentable sugars from the grains and separating the wort from the spent grain material, which is necessary for subsequent fermentation steps in the brewing process.
What is a separate tank?
A separate tank refers to a vessel or tank that is used for a specific step in the brewing process, distinct from other stages. Rather than combining multiple functions within a single vessel, separate tanks are dedicated to individual processes, allowing for more focused control and flexibility.
Here are a few examples of separate tanks commonly used in brewing:
Mash Tun: The mash tun is a separate tank used specifically for the mashing process. It holds the crushed malted grains and hot water, providing the ideal environment for enzymatic conversion of starches into fermentable sugars. The mash tun is equipped with temperature controls and agitators to facilitate the mashing process.
Lauter Tun: The lauter tun is another separate tank used for the lautering process, which involves separating the liquid wort from the spent grain material after mashing. The lauter tun typically has a false bottom or perforated plate system that acts as a filter to allow the wort to flow through while retaining the grain solids.
Brew Kettle: The brew kettle, also known as the boiling kettle or simply the kettle, is a separate tank dedicated to the boiling and hopping of the wort.
Whirlpool tank: The whirlpool tank is a separate vessel used after boiling to create a whirlpool effect in the wort. The whirlpooling process helps separate the trub (coagulated proteins, hop particles, and other solids) from the liquid wort. The clarified wort can then be transferred to the fermentation vessel or cooled further.
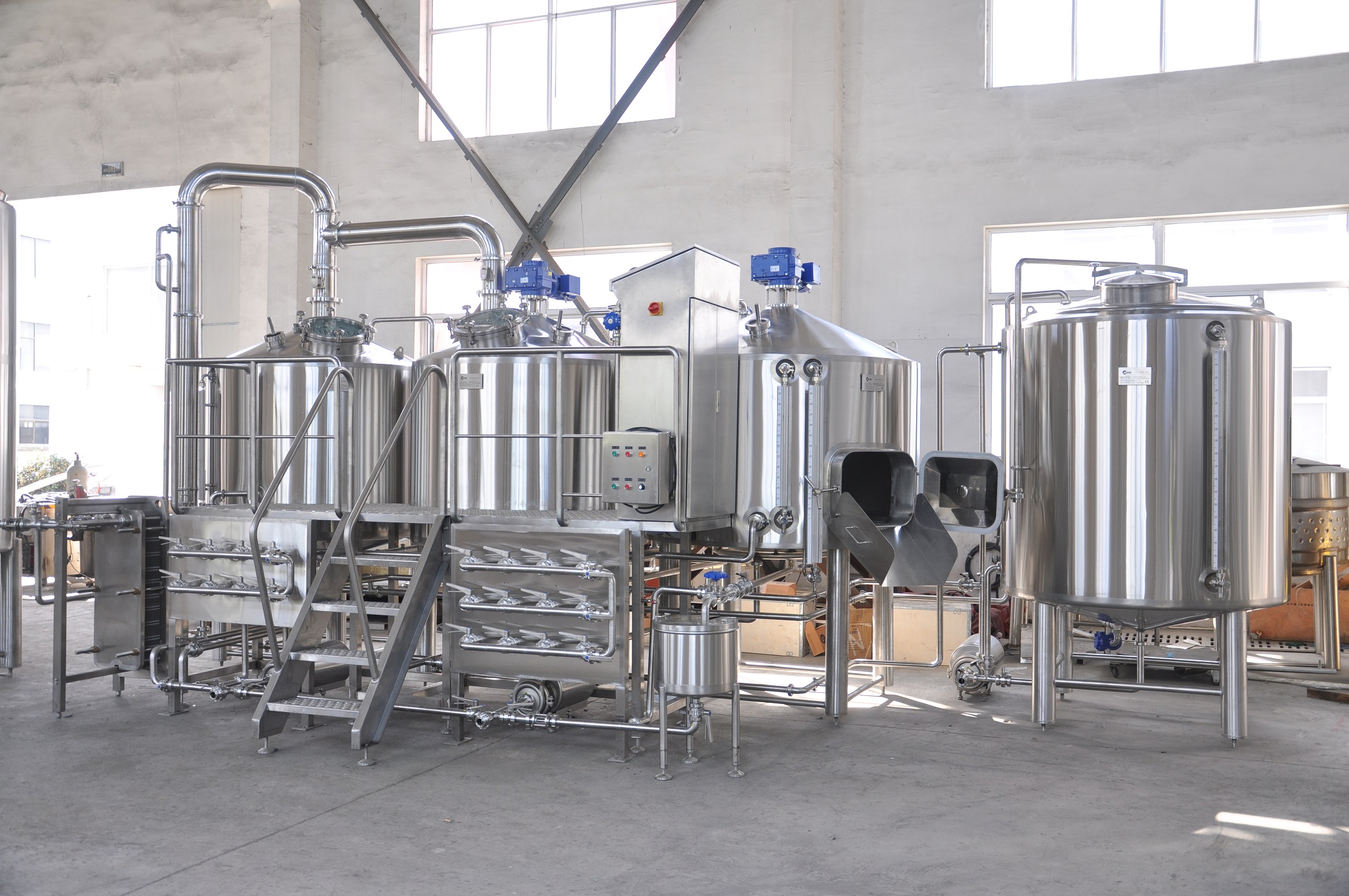

Which container should be to choose?
Here are some considerations for each option:
Combination Mash/Lauter Tanks:
Efficiency: Combination tanks allow for a continuous brewing process, where mashing and lautering occur in the same vessel. This can result in improved efficiency and time savings as there is no need to transfer the mash to a separate vessel for lautering.
Space and Cost: Using a single combination tank instead of separate vessels can save space and reduce equipment costs. It requires fewer vessels and piping arrangements, making it suitable for smaller breweries or those with limited space.
Control: With a combination tank, brewers have less control over the mashing and lautering processes individually. This may be a consideration if you require precise control over each step or want to experiment with different techniques for mashing and lautering.
Workflow Streamlining: Using a combination tank allows for a more streamlined brewing process since there is no need to transfer the mash from one tank to another. It simplifies the process and reduces the risk of contamination or loss of heat during transfer.
Separate Mash and Lauter Tanks:
Flexibility: Having separate mash and lauter tanks allows for more flexibility in the brewing process. Brewers can optimize each step independently, adjusting mash temperatures, agitation, and lautering techniques to achieve desired flavors, extract efficiency, and clarity.
Process Control: By separating the mashing and lautering processes, brewers have greater control over factors such as wort clarity, grain bed filtration, and sparging efficiency. This can be beneficial when brewing specific beer styles or aiming for consistent results.
Simultaneous Operations: If you have the equipment and space, using separate tanks allows for simultaneous operations. While lautering is taking place, the mash tank can be freed up for the next brewing cycle, increasing overall brewing capacity.
Troubleshooting: In the event of issues during either mashing or lautering, having separate tanks makes it easier to identify and address the problem without disrupting the entire brewing process.
Specialized Equipment: Lauter tanks can be designed specifically for optimal lautering, with features such as false bottoms, rakes, or screens. Having a dedicated lautering vessel can enhance efficiency and help achieve desired wort clarity.
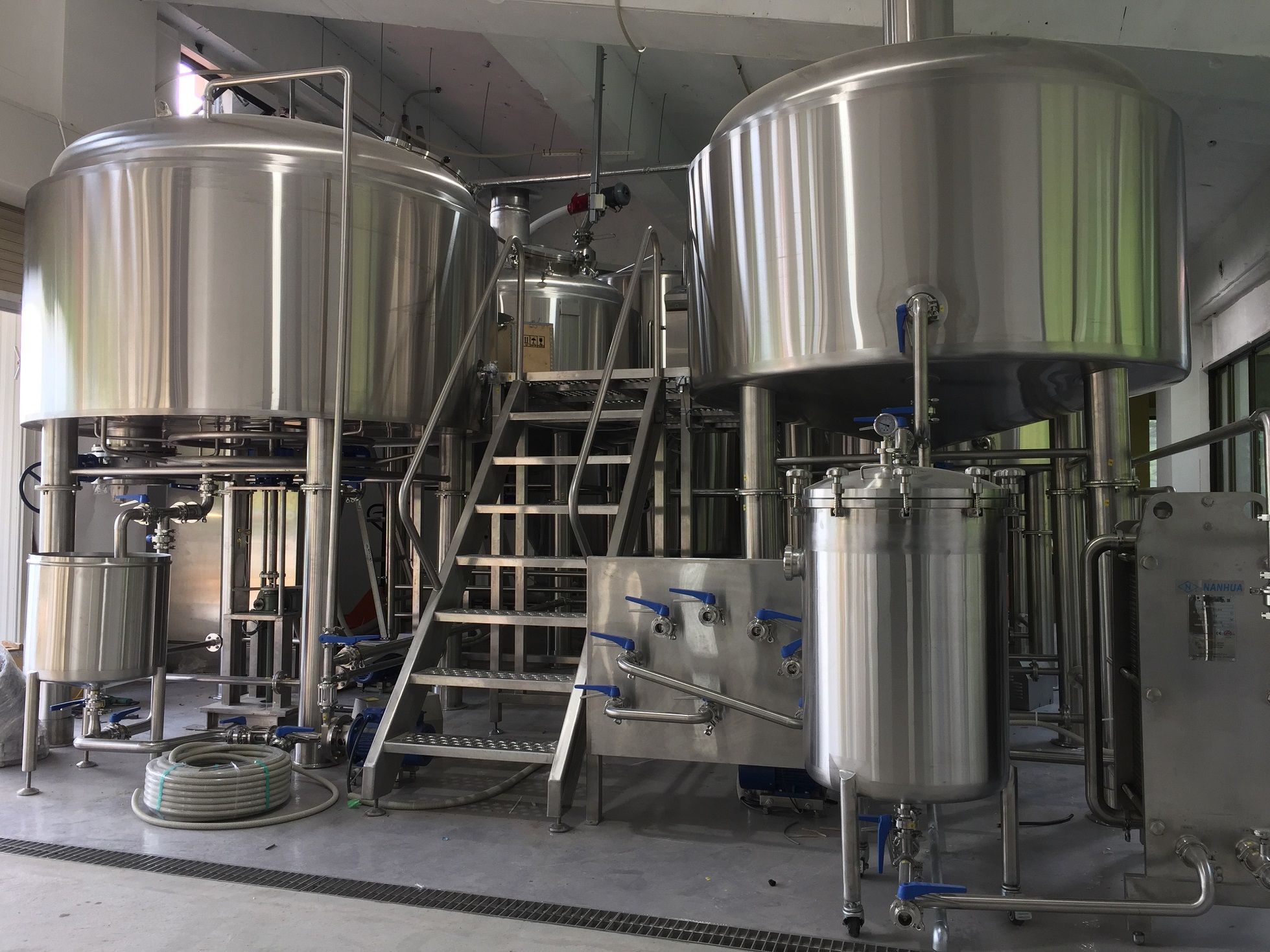

It’s important to note that both approaches have their merits and are widely used in different breweries. The choice ultimately depends on the specific needs, scale, and preferences of the brewery, as well as the available equipment and space constraints.