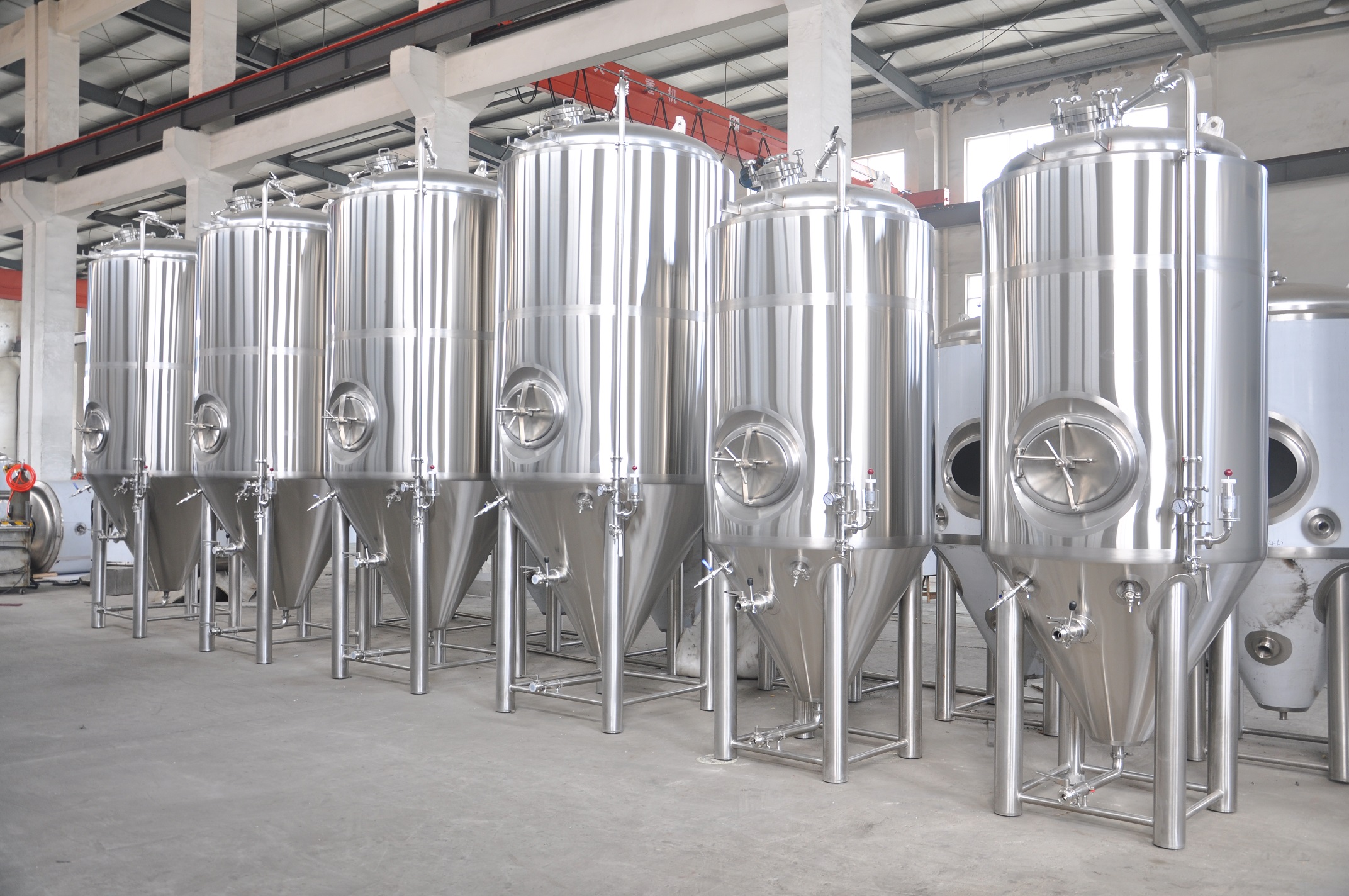
Superior Stainless Steel Beer Fermenter: The Perfect Choice for Exceptional Brewing
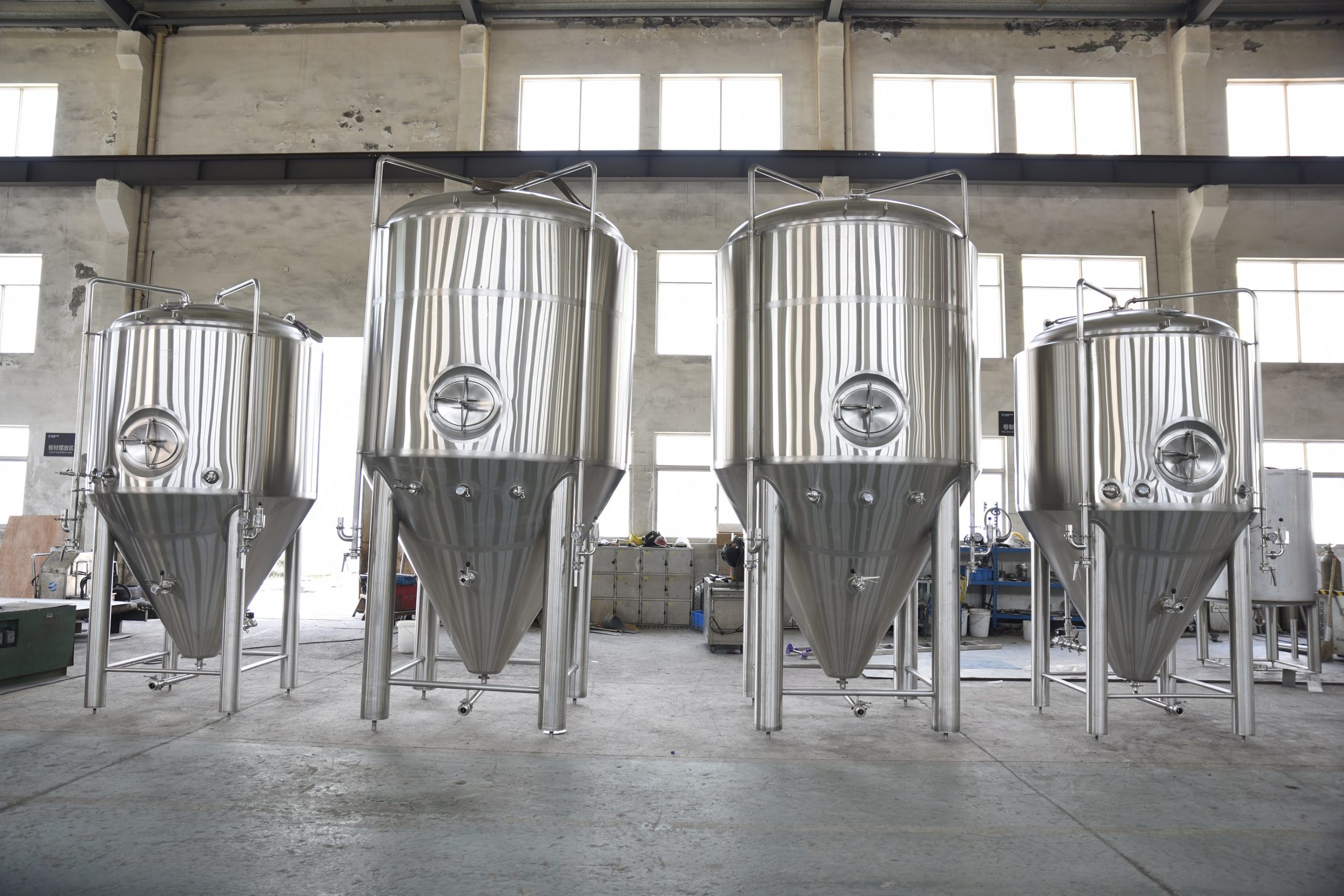

A stainless steel beer fermenter is a vessel used in the brewing process to ferment beer. It is typically made of stainless steel, which offers durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. Stainless steel fermenters are preferred by many brewers due to their ability to maintain proper temperature control, prevent contamination, and withstand the pressures generated during fermentation. in this article, we’ll dive into everything you need to know about stainless steel beer fermenter, from their advantage to the different types and sizes available. We’ll also cover how to properly use and maintain your stainless steel beer fermenter, so you can ensure the best quality beer every time.
Advantages of using a stainless steel beer fermenter
Using a stainless steel beer fermenter offers several advantages:
Durability: Stainless steel is a robust material that can withstand frequent use and handling without deteriorating or compromising its structural integrity.
Corrosion resistance: Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust and corrosion, ensuring that the fermenter remains in good condition even when exposed to moisture and acidic substances during fermentation.
Ease of cleaning and sanitation: Stainless steel surfaces are smooth and non-porous, making them easy to clean and sanitize effectively. This reduces the risk of contamination and helps maintain a high level of hygiene during the brewing process.
Temperature control: Stainless steel has excellent thermal conductivity, allowing for efficient temperature control during fermentation. It can quickly cool down or heat up, depending on the brewing requirements, facilitating the desired fermentation conditions.
Oxygen impermeability: Stainless steel is impermeable to oxygen, preventing unwanted oxygen exposure during fermentation. This is crucial for maintaining the flavor and aroma integrity of the beer.
Pressure resistance: Fermentation produces carbon dioxide, which generates pressure inside the fermenter. Stainless steel is strong enough to withstand the pressure, ensuring a safe and secure environment for fermentation.
Longevity: Stainless steel fermenters have a long lifespan due to their durability and resistance to wear and tear. They can withstand repeated use over an extended period, making them a cost-effective investment for breweries.
Aesthetic appeal: Stainless steel fermenters often have a sleek and professional appearance, which can enhance the visual appeal of a brewery and create a positive impression on customers.
Overall, using a stainless steel beer fermenter provides brewers with a reliable and efficient fermentation vessel that helps maintain the quality and integrity of their beer throughout the brewing process.
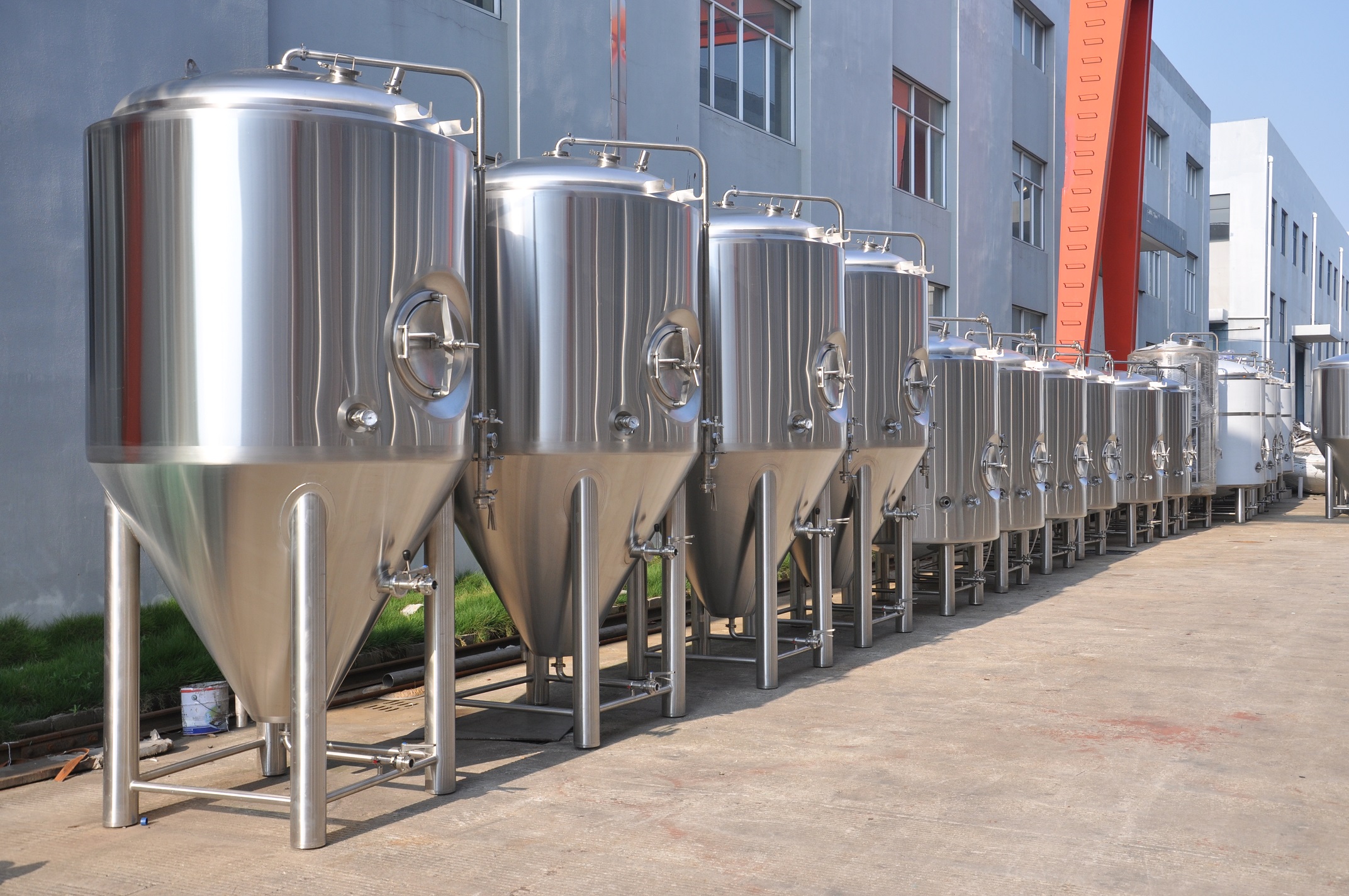

Types of stainless steel beer fermenters
There are several types of stainless steel beer fermenters available, catering to different brewing needs and preferences. Here are some common types:
Conical Fermenters: These fermenters have a conical shape, with a pointed bottom that allows sediment and yeast to settle at the bottom. They often feature a separate outlet for easy removal of the sediment, and some models have built-in temperature control options.
Unitank fermenters: Uni-tanks, short for “universal tanks,” are versatile fermenters that can be used for both fermentation and maturation of beer. They typically have a conical shape and may include features such as pressure relief valves, temperature gauges, and carbonation options.
Brite Tanks: Brite tanks, also known as bright beer tanks or conditioning tanks, are used for the final stages of beer production. They are designed to store, carbonate, and clarify the beer before it is packaged. Brite tanks often have a cylindrical shape and may include carbonation stones or sight glasses.
Fermentation Vessels with Glycol Jackets: These fermenters have an added glycol jacket surrounding the tank. This jacket allows for precise temperature control during fermentation by circulating cold or warm glycol through the jacket. They are commonly used in professional breweries where temperature control is crucial.
Stackable Fermenters: Stackable fermenters are compact and designed to save space in breweries with limited floor space. They can be stacked vertically, allowing multiple fermenters to be used in a smaller footprint.
Open-top fermenters: Open-top fermenters are large vessels without a sealed lid. They are commonly used in traditional brewing methods, such as open fermentation in the production of certain beer styles like Belgian ales or lambics. Open-top fermenters provide increased exposure to ambient air and yeast, contributing to unique flavor and aroma profiles.
Cylindrical fermenters: Cylindrical fermenters have a cylindrical shape with a flat or slightly sloping bottom. They are often used in commercial breweries and can be equipped with various features such as cooling jackets, pressure relief valves, and sample ports.
Customizable Fermenters: Some manufacturers offer customizable stainless steel fermenters that can be tailored to specific brewing requirements. These may include options for different sizes, configurations, fittings, and additional features such as racking arms, sampling valves, or sight glasses.
These are just a few examples of stainless steel beer fermenters. The choice of fermenter depends on the specific needs, scale, and preferences of the brewer or brewery.
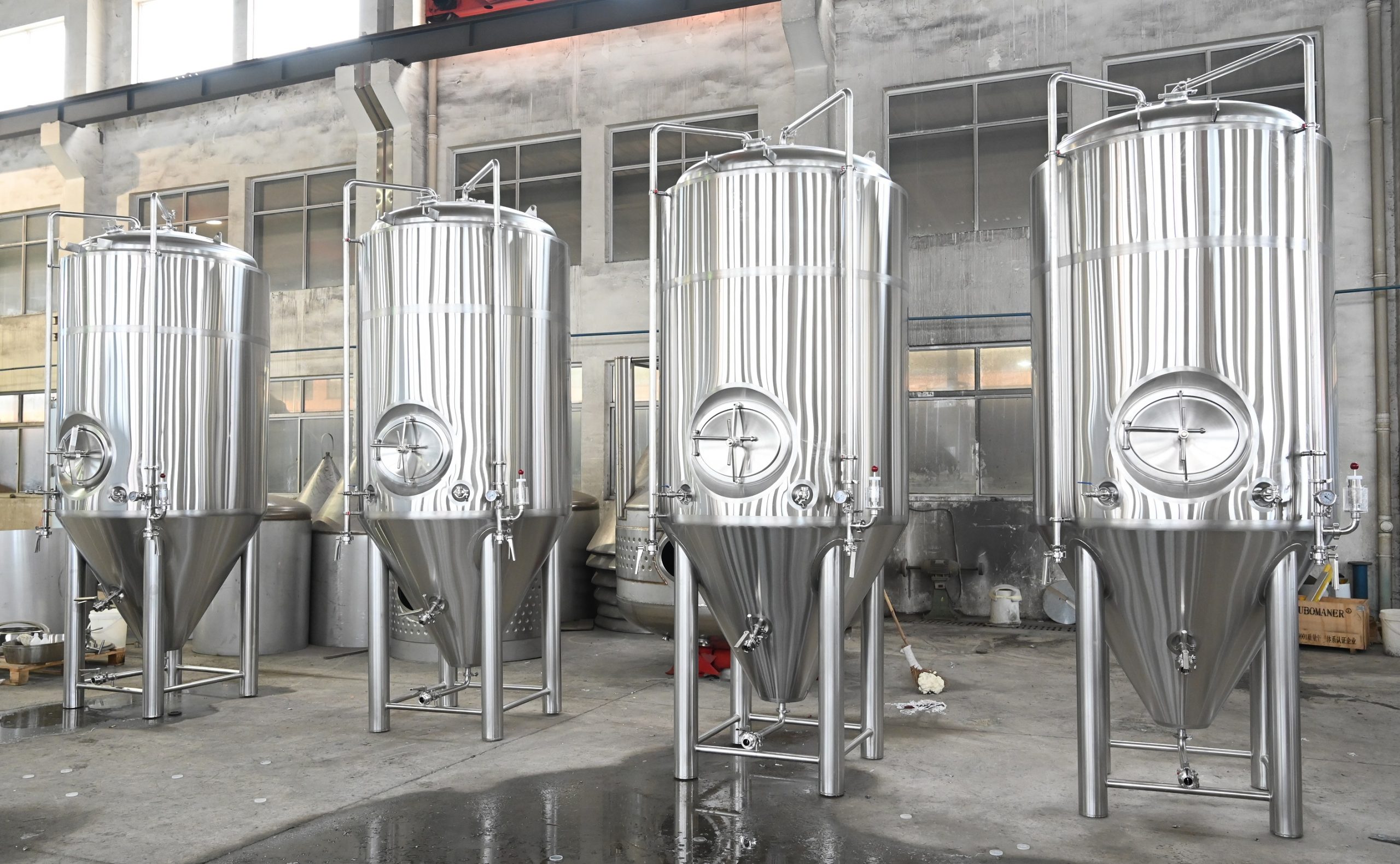

Choosing the right size for stainless steel beer fermenters
Choosing the right size for a stainless steel beer fermenter depends on various factors, including the batch size, production volume, and future growth plans of the brewery. Here are some considerations when determining the appropriate size:
Batch size: Determine the desired batch size for your brewing operations. This can range from small homebrew sizes (e.g., 5 gallons) to larger commercial sizes (e.g., 10 barrels or more). Ensure that the fermenter can accommodate the desired batch size without excessive headspace, which can lead to oxidation or off-flavors.
Production volume: Consider the anticipated production volume of your brewery. If you plan to produce larger quantities of beer, you may require multiple fermenters or larger capacity fermenters to meet demand efficiently.
Future growth: Take into account your brewery’s growth plans. If you anticipate expanding production in the future, it may be wise to invest in larger fermenters to accommodate increased brewing volumes without the need for immediate upgrades.
Available space: Assess the physical space available in your brewery. Consider the dimensions and footprint of the fermenters to ensure they fit comfortably and allow for proper workflow and maintenance.
Brewing schedule: Evaluate your brewing schedule and turnaround time. If you aim to brew multiple batches simultaneously or have a rapid turnover of batches, having multiple fermenters of appropriate size can help maintain production efficiency.
Equipment compatibility: Ensure that the chosen fermenter size aligns with the capacity of other brewing equipment, such as mash tuns, boil kettles, and packaging equipment, to maintain a smooth brewing process and avoid bottlenecks.
Cost considerations: Keep in mind that larger fermenters typically come with a higher price tag. Consider your budget and weigh the cost of acquiring and operating larger fermenters against the potential benefits and growth opportunities they offer.

How to using and maintaining of stainless steel beer fermenters
Using and maintaining stainless steel beer fermenters involves several steps to ensure proper operation and longevity. Here’s a general guide:
Cleaning before use: Before using a new stainless steel fermenter or after each fermentation cycle, thoroughly clean the fermenter using a brewery-approved cleaning agent. Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer or supplier. Rinse the fermenter with clean water to remove any residue from the cleaning process.
Sanitization: Prior to transferring the beer into the fermenter, sanitize the vessel to eliminate any potential sources of contamination. Use a brewery-grade sanitizer following the recommended dilution and contact time specified by the sanitizer manufacturer.
Transferring and fermentation: Transfer the cooled wort into the sanitized fermenter. Seal the fermenter tightly to prevent oxygen or other contaminants from entering. Place an airlock or blow-off tube on the fermenter to allow carbon dioxide to escape during fermentation while maintaining a barrier against outside air.
Temperature control: Maintain the desired fermentation temperature by monitoring and adjusting the ambient temperature or using a cooling system if your fermenter has cooling capabilities. Ensure that the fermenter is placed in a suitable location away from direct sunlight, excessive heat, or extreme temperature fluctuations.
Monitoring and measurements: Regularly monitor the progress of fermentation by taking gravity readings, checking temperature, and observing the activity in the airlock or blow-off tube. Adjust temperature or other parameters as needed based on the specific beer style and fermentation requirements.
Yeast management: If using reusable yeast, ensure proper yeast handling and pitching rates. Follow best practices for yeast rehydration, propagation, and storage to maintain yeast health and vitality.
Post-fermentation: After fermentation is complete, transfer the beer to a secondary vessel, such as a brite tank or kegs, for conditioning or packaging. Clean and sanitize the fermenter promptly to remove any remaining residue or yeast sediment.
Routine maintenance: Regularly inspect the fermenter for any signs of wear, damage, or leakage. Clean and sanitize all fittings, valves, and seals. Replace any worn or damaged components promptly to ensure proper functionality and prevent contamination risks.
Storage: When not in use, store the fermenter in a clean and dry environment to prevent corrosion or damage. Cover or protect the fermenter from dust, pests, and any potential sources of contamination.
Periodic deep cleaning: Perform periodic deep cleaning of the fermenter to remove stubborn deposits or stains. Use specialized cleaning agents or procedures recommended by the manufacturer or supplier. Follow proper safety precautions and guidelines during deep cleaning.
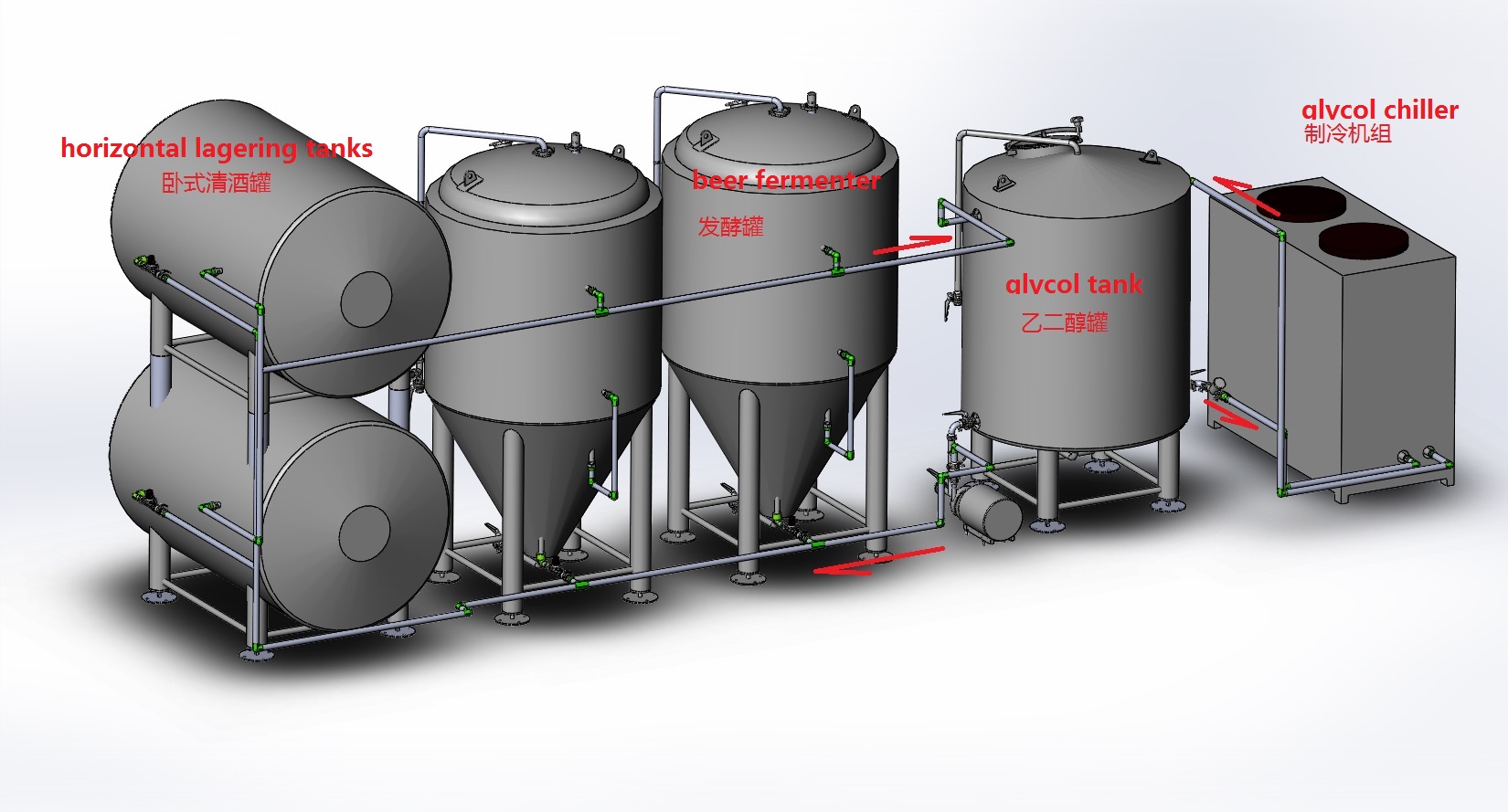
Conclusion
The advantages and features of stainless steel beer fermenters, so investing in stainless steel beer fermenters can be a smart decision, especially if you are considering starting a commercial brewery or expanding an existing one. But remember to conduct thorough market research, financial analysis, and consult with industry experts before making any investment decisions.